Article


A range of potentially malignant disorders is recognized but erythroplakia (erythroplasia), leukoplakia and lichenoid lesions are the most important. Others, such as actinic cheilitis, discoid lupus erythematosus, submucous fibrosis, Fanconi anaemia (syndrome) and other lesions are important but generally less common (Table 1).
| Malignant potential | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Very high | High | Low | |
| Main entities | Erythroplakia | Leukoplakia |
Leukoplakia |
| Uncommon entities | Actinic cheilitis, |
Discoid lupus |
|
Our inability to be able to define the risk of malignant transformation of a potentially malignant oral lesion for an individual patient is one of the biggest challenges in the field, as is the inability to reliably predict the effects of any treatments. Sadly, the evidence base is missing.
It is even more crucial, therefore, to ensure that the patient gives fully informed consent to the management decided after full discussion with the clinician.
This article focuses on erythroplakia, leukoplakia and lichenoid lesions/lichen planus.
Erythroplakia
Erythroplakia is rare (<1.0%), typically related to tobacco and alcohol use, and seen in the middle-aged and the older patient. It is usually a solitary lesion defined as a ‘fiery red patch that cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other definable disease’. The clinical appearance is often of a flat or even depressed erythematous area of mucosa and for that reason the term ‘erythroplasia’ may be more appropriate (Figure 1). In some, there is a mixture of red and white changes – when the lesion is termed ‘erythroleukoplakia’ or non-homogeneous leukoplakia.
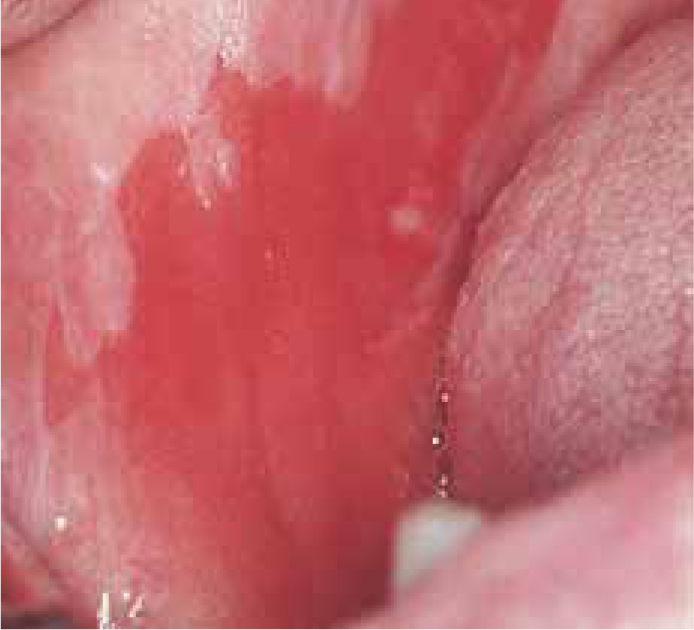
Histopathologically, erythroplakia frequently shows at least moderate or severe dysplasia and the majority will undergo malignant transformation. Erythroplakia needs to be removed by surgery, usually either by cold knife (scalpel) or by laser excision, and the specimen sent for histopathological examination, but there are no reliable data about the recurrence rate.
Leukoplakia
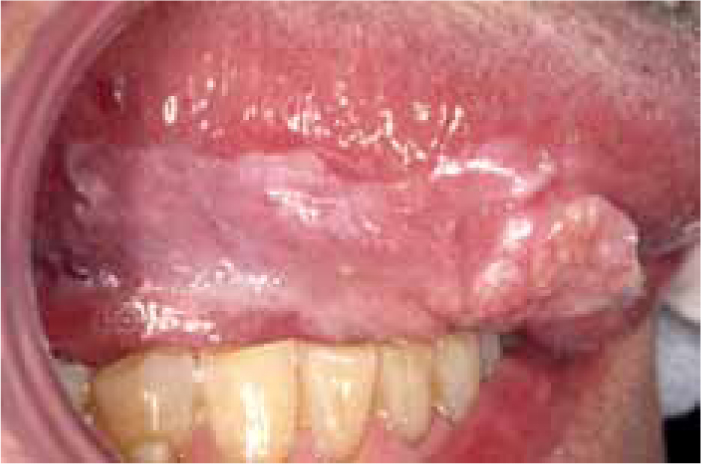
Leukoplakia is more common than erythroplakia (~2%) and is associated with tobacco, alcohol and possibly papillomavirus. Defined as ‘A white plaque of questionable risk having excluded (other) known diseases or disorders that carry no increased risk for cancer’, it can be confused with other white lesions, such as amalgam-associated leukoplakic or lichenoid lesions. By definition, the term excludes entities such as frictional keratosis, smokers keratosis and lichenoid lesions.
Leukoplakia can appear clinically as:
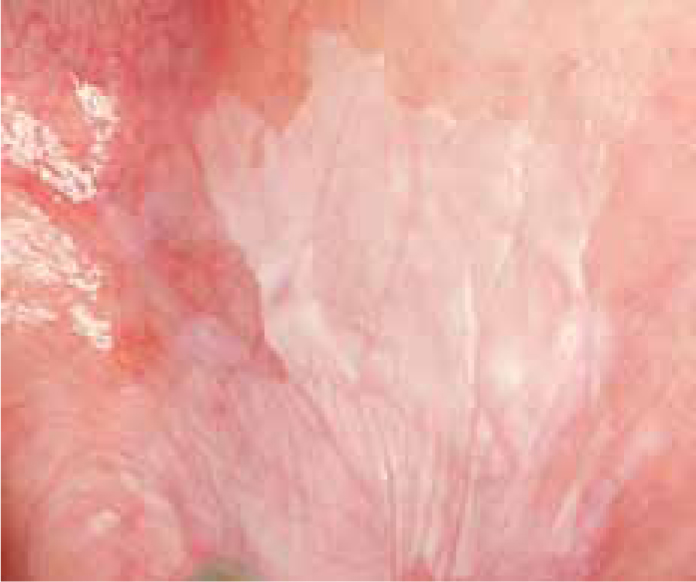
In the assessment and quantification of epithelial dysplasia, a distinction is commonly made between dysplastic and non-dysplastic leukoplakias, although there may be considerable intra- and inter-observer variation among histopathologists. An annual malignant transformation rate of about 1–2% is probably a realistic figure for all types of leukoplakia together. Epithelial dysplasia – often correlating with a non-homogeneous, erythroleukoplakic clinical appearance – is in general regarded as the most important indicator of malignant potential. In dysplastic leukoplakias, the malignant transformation may reach 30% (Figure 4).
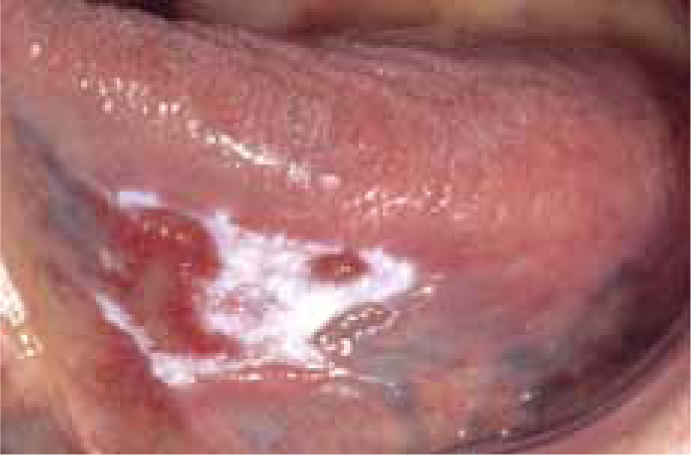
In any potentially malignant lesion such as a leukoplakia, however, there might be a range of cells present of different malignant potential, including some that cross the epithelial basement membrane – defining the lesion as cancer (Figure 5).
Thus the histopathological interpretation of a biopsy from such a lesion could vary from benign to malignant, depending on the site biopsied, the histopathologists acumen, and other factors. Total reliance on a biopsy result, therefore, could be fraught. Indeed, more than 25 years ago, one study showed that oral leukoplakias which were non-dysplastic upon incisional biopsy proved, in around 10% of cases, to contain cancers on excision of the leukoplakias. Similar findings were reported more recently by a different group of investigators.
It is also not possible at present to predict which dysplastic lesions will progress to carcinoma reliably, nor to be absolutely certain that a clinical lesion has malignant potential or not. Over the past few years, much effort has gone into identifying genetic changes that may underlie oral carcinoma and to find biomarkers, such as DNA ploidy, and changes in p53, and chromosomes 3 and 9 that might predict neoplastic change. Unfortunately, none has yet been shown to be absolutely reliable – but these or other markers will, in the future, surely not only add to our understanding of the pathobiology of malignant transformation, but help diagnostically and prognostically.
We can conclude therefore that, at least at present, there are no signs or symptoms which reliably predict whether a leukoplakia will undergo malignant change, though suggestive features are the presence of:
Known risk factors for malignant transformation are listed below:
The evidence from systematic reviews is that medical therapies are not reliably effective: topical anti-cancer agents or retinoids, though generally well tolerated, have only temporary efficacy, and perhaps their best indication is when the location or extent of the lesion render surgical removal difficult. Topical treatment with podophyllin or bleomycin has induced some regression or even total resolution, but lesions recur.
An algorithm for the management of leukoplakia is presented in Figure 6. Biopsy confirmation is essential. Possible aetiological factors should be removed, and an observation of 2–4weeks seems acceptable to observe any possible regression. The authors are of the opinion that it is best to remove all non-regressing leukoplakias if feasible, irrespective of the reported presence or absence of epithelial dysplasia on biopsy, despite there being no scientific evidence that treatment truly prevents the possible future development of a squamous cell carcinoma. This seems wiser than ‘watchful waiting’.
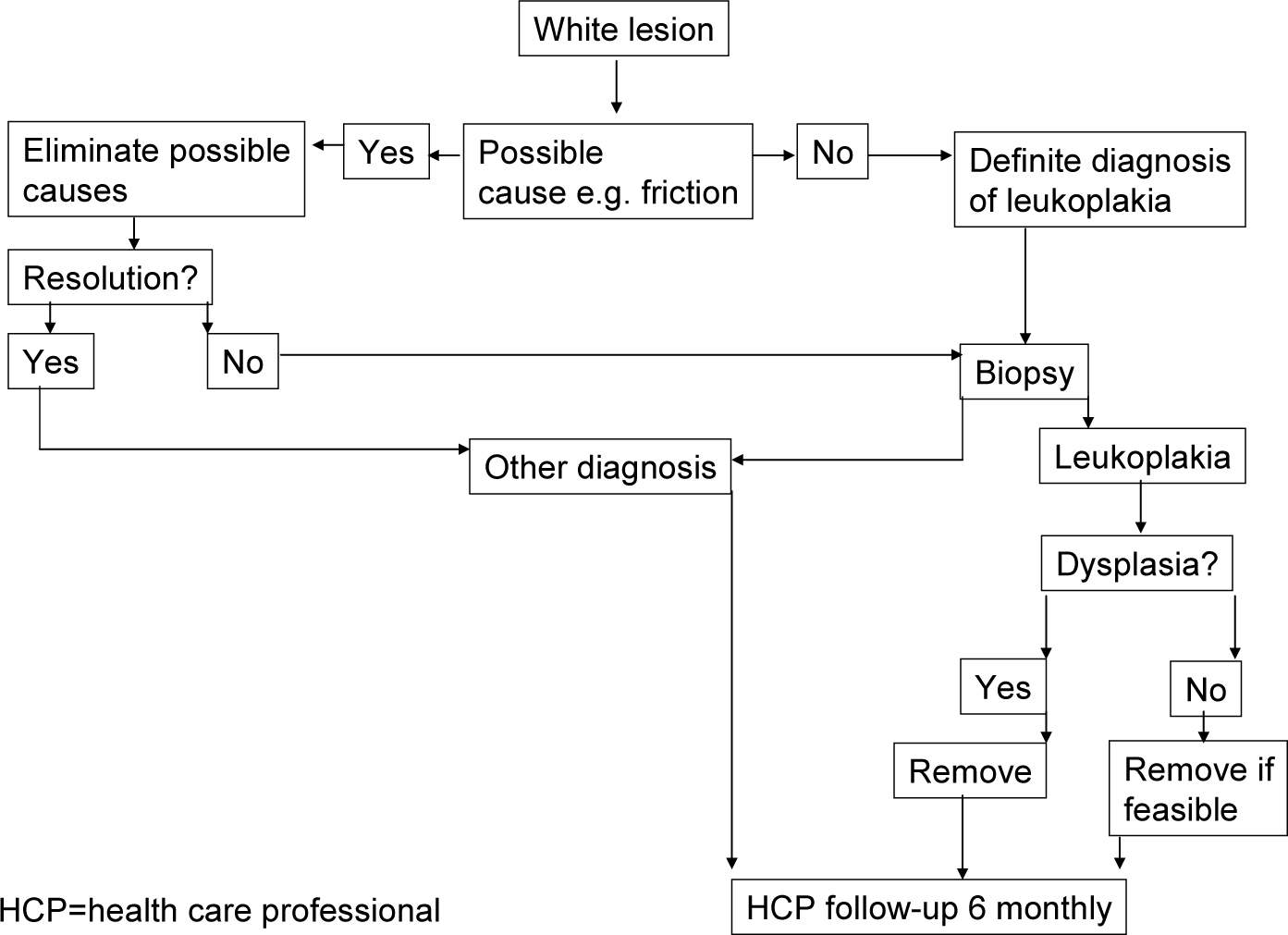
The most commonly used treatment modalities include surgical or CO2 laser excision with the specimen sent for histopathological examination. In widespread leukoplakias, photodynamic therapy may be considered. Recurrence rates may be up to 30%, probably mainly depending on the duration of follow-up.
The efficacy of continuous follow-up of oral leukoplakia patients is virtually unknown.
Lichen planus
Oral lichen planus (OLP) is also regarded as a potentially malignant disorder, but with an annual malignant transformation rate less than 0.5%. Transformation may occur in any of the clinical types of OLP.
Unfortunately, there are no strategies that can prevent this malignant transformation and the efficacy of continuous follow-up of OLP patients, although recommended by various authors, is questionable.
