Article



Specialist referral may be indicated if the Practitioner feels:
Salivary gland swelling
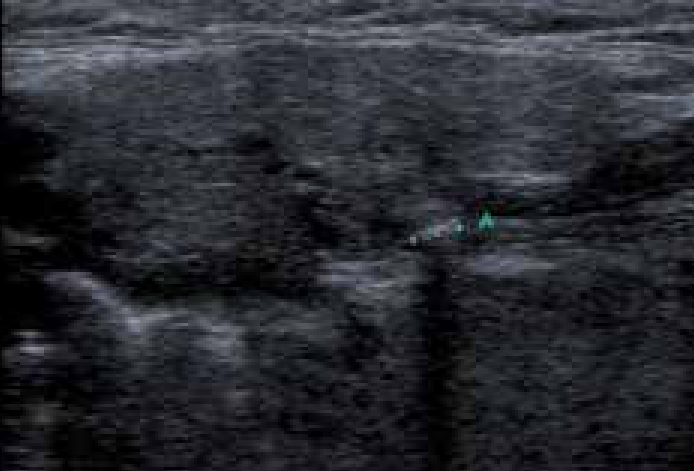
Salivary glands usually swell because of inflammation (sialadenitis) (Figure 1), which is often viral but may have other causes (Table 1). Obstruction of salivary flow is another common cause (obstructive sialadenitis) (Figures 2, 3). Rare causes include salivary gland or other neoplasms (Figures 4–7).
|
|
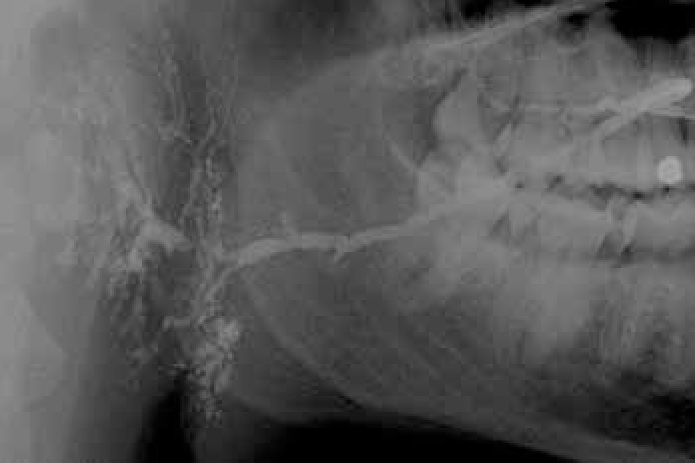
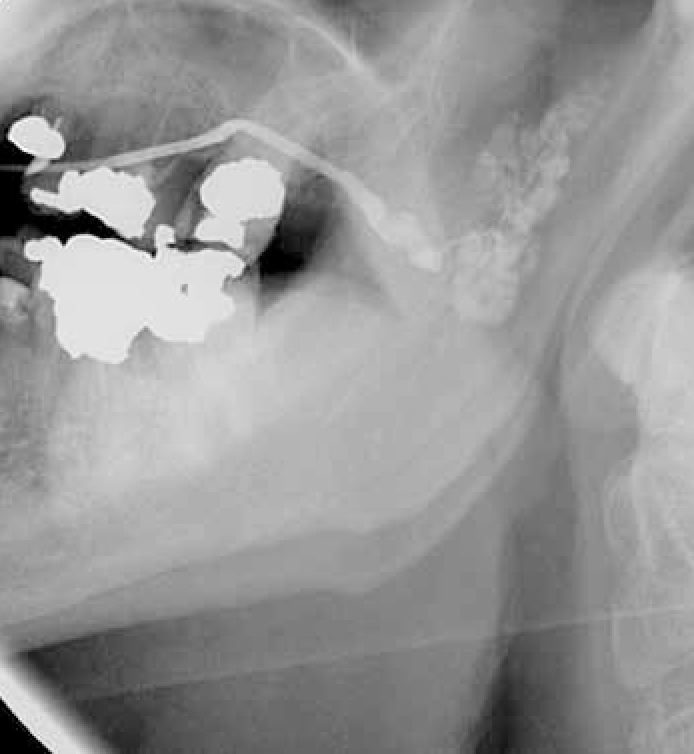
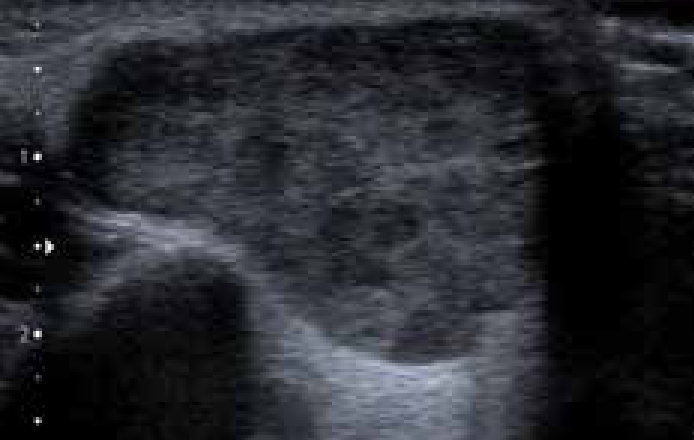
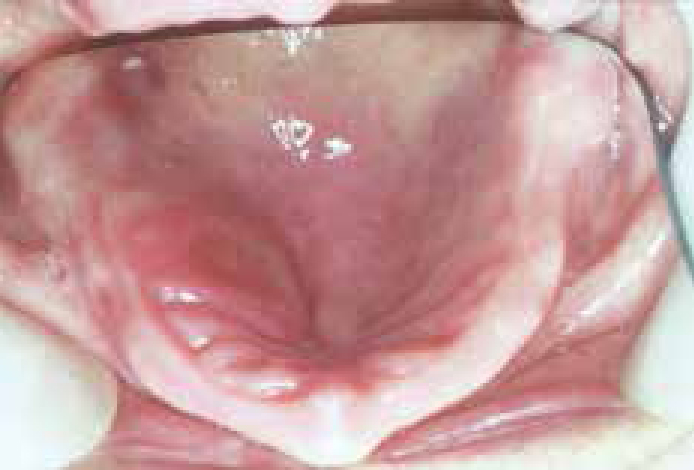
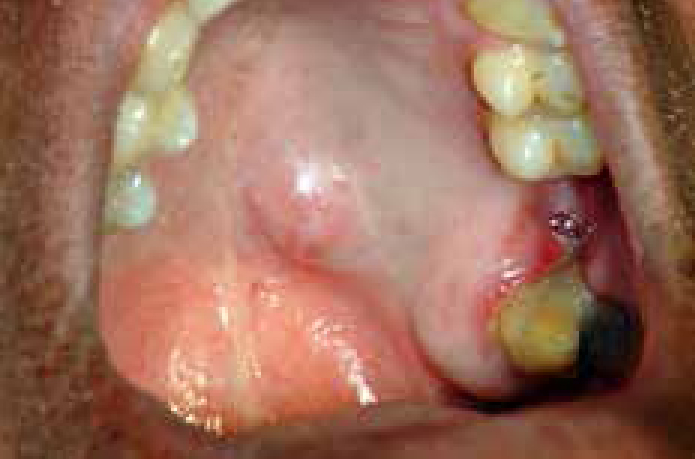
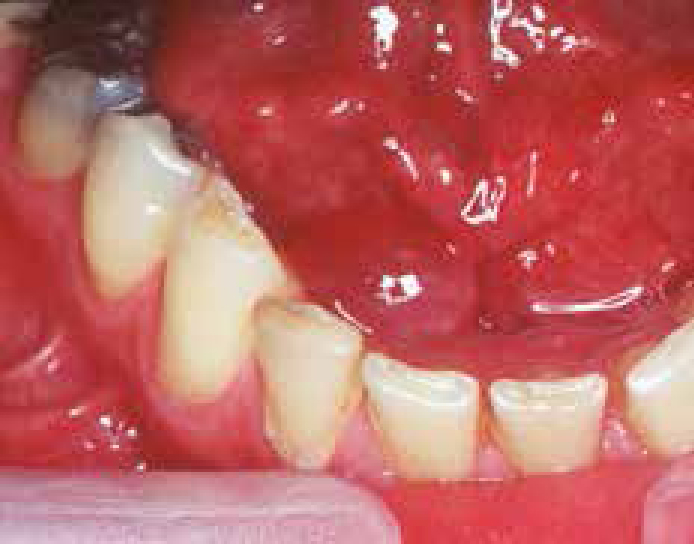
In children, most salivary gland swellings are caused by mucoceles or mumps. In adults, most swellings of the salivary glands are caused by mucoceles (Figure 8), salivary duct obstruction (typically by a stone); but sialadenitis, Sjögren's syndrome and neoplasms are important causes to be excluded.
Diagnosis of salivary gland swelling
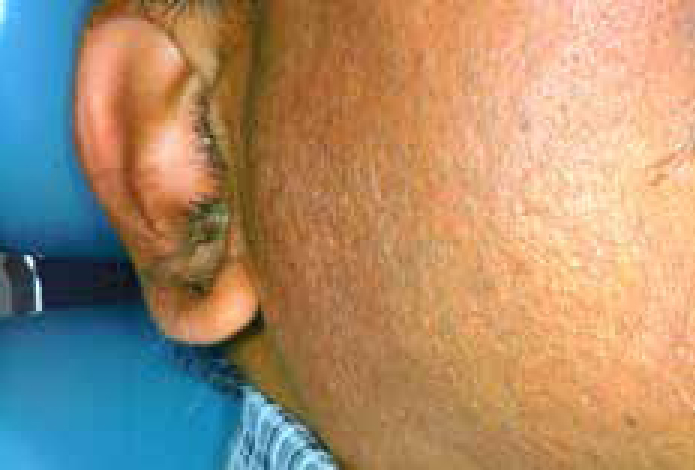
It can be difficult to establish whether a major salivary gland is genuinely swollen, especially in obese patients. A useful guide to whether the patient is simply obese or has parotid enlargement is to observe the outward deflection of the ear lobe, which is seen in true parotid swelling.
Diagnosis of the cause is mainly clinical but investigations such as imaging (especially ultrasound), liver function tests, serology for viral antibodies autoantibodies or biopsy, may be indicated.
Management
A specialist opinion is usually needed and treatment is of the underlying cause.
Immediate treatment is needed for acute bacterial sialadenitis; under ideal conditions antimicrobial therapy should be determined by results of culture and sensitivity of a sample of pus from the duct. However, as first line therapy a penicillinase-resistant penicillin such as flucloxacillin is appropriate. In patients with penicillin allergy, erythromycin is a suitable alternative. In addition, general supportive measures such as analgesia and increased fluid intake are important. Thereafter, specialist referral is generally indicated to identify any predisposing factors. Neoplasms need Specialist attention.
