Abstract
This paper describes the use of subepithelial connective tissue graft with platelet rich plasma in the treatment of gingival recession. There was complete root coverage in both the cases and the coverage is still maintained after 4 years.
From Volume 39, Issue 3, April 2012 | Pages 218-220
This paper describes the use of subepithelial connective tissue graft with platelet rich plasma in the treatment of gingival recession. There was complete root coverage in both the cases and the coverage is still maintained after 4 years.

A variety of surgical techniques has been described to cover exposed root surfaces and these procedures were organized into various categories in a consensus report in 1996.1 The subepithelial connective tissue graft (SECTG), as described by Langer and Langer, predictably increased root coverage of Class I and II recession by more than 90%.2
Using platelet-rich plasma (PRP) involves taking a sample of a patient's blood pre-operatively, concentrating autologous platelets and applying the resultant gel to the surgical site. Surgical sites applied with PRP have been shown to heal two to three times faster than normal surgical sites.3 PRP delivers a highly concentrated dose of autologous platelets containing a variety of biologic mediators that can be applied directly to the healing site. It is also believed that the PRP accelerates soft tissue healing by promoting a more rapid revascularization and re-epithelialization of flaps and cell proliferation. In an attempt to increase the success rate of connective tissue grafting, as well as to increase the successful use of tissue regeneration membranes to provide root coverage, incorporation of the platelet-rich plasma into the surgical protocol was advocated.4
The two patients selected for this study were free from any systemic disease. One had a Class I gingival recession and the second had a Class II gingival recession in the anterior quadrant with ≥2 mm of loss of attachment. Both had radiographic evidence of sufficient interdental bone (the distance between crestal bone and CEJ ≤2 mm).
The recession width, depth and keratinized gingiva were measured pre-surgically and post-surgically. The patients were recalled at 14 days, 4 weeks, 3 months and 6 months post-operatively. Oral hygiene instructions were reinforced at every visit. The amount of coverage was measured at the end of six months.
The selected patients underwent phase I therapy and occlusal adjustments were done in cases of traumatic occlusion. Detailed instructions regarding self-performed plaque control measures were given. An informed consent was taken from each patient.
Blood was taken from the anticubital region with a 21 gauge needle and syringe and collected into the 10 mL blood collection tube – the vacutainer, containing trisodium citrate anticoagulant. The blood and anticoagulant were properly mixed by inverting the tube.
The tubes were centrifuged for 10 minutes at 2,400 rpm to produce platelet-poor plasma (PPP). This resulted in separation of the whole blood into PPP, buffy coat and erythrocytes. The PPP was taken into a syringe with a long cannula and transferred into another tube. The remaining blood was subjected to second centrifugation for 15 minutes at 3,600 rpm to concentrate platelets. The second supernatant was also taken out with the help of another long cannula; that was the PRP.
At the time of the application, the PRP was activated by combining with an equal volume of a sterile saline solution containing 10% calcium chloride and 100 U/mL of sterile thrombin (an activator that allows polymerization of the fibrin into an insoluble gel).
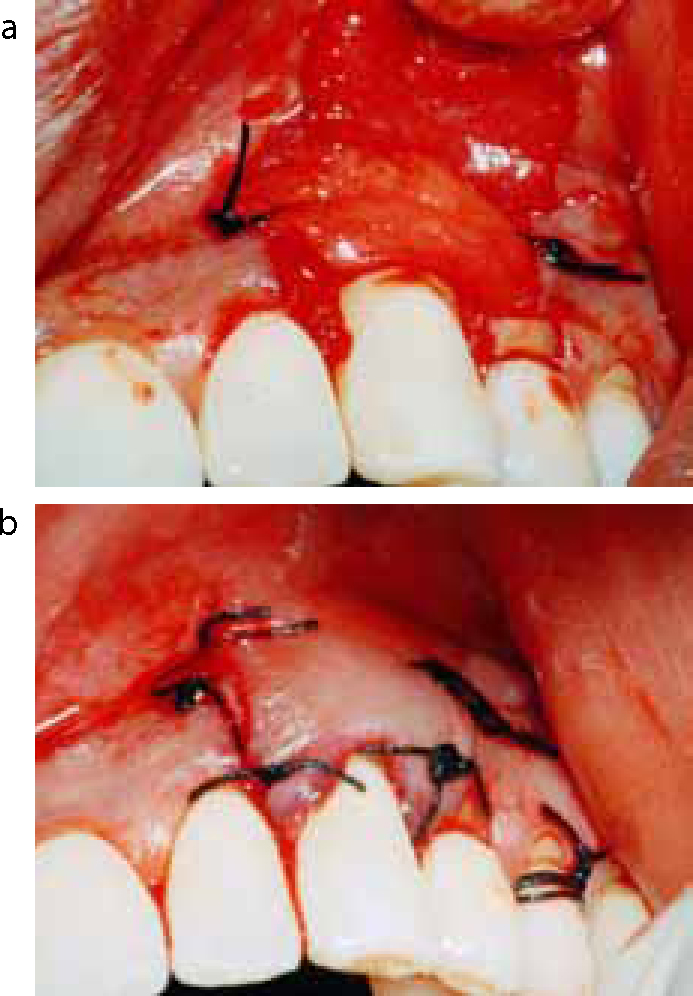
The operative site (Figure 1) was anaesthetized with 2% Lidocaine HCl with adrenaline (1: 80,000), using block and infiltration techniques. The crevicular incisions were made on the facial side of the tooth involved with recession. Two vertical incisions were made on the adjacent line angles of the teeth extending beyond mucogingival junction. A full thickness mucoperiosteal flap was reflected to the mucogingival junction by using the periosteal elevator. After reflection of the full thickness flap and exposure of the bone on the buccal surface, the flap was continued as a partial thickness flap beyond the mucogingival junction. Sharp dissection was done to relieve the flap for coronal advancement (Figure 2). The root surface was planed with curettes.

The size of graft required was obtained with a surgical template. After preparation of the recipient bed, the donor area in the palate was anaesthetized by block anaesthesia of the greater palatine and nasopalatine nerves with 2% Lidocaine HCI containing 1:80,000 adrenaline. The technique, described by Bruno,6 was used to harvest connective tissue graft (CTG) from the palate.
The CTG was placed on the saline-soaked gauze and the palatal wound was closed with horizontal crossed/parallel suspension sutures. The 1–2 mm of epithelial collar at the coronal aspect of the donor tissue and all adipose tissue was removed and discarded.
After the required amount of connective tissue graft was harvested, the tissue was coated with PRP to allow the growth factors to impregnate the connective tissue graft. Subsequently, PRP was also applied to the exposed and prepared root surfaces.
The connective tissue graft was sutured at the recipient site using non-resorbable silk sutures. The flap was coronally advanced and sutured so that the graft was completely submerged under the flap (Figure 3).
The surgical area was protected with a non-eugenol dressing (Coe pak, GC America Inc, USA). All patients were prescribed systemic Doxycycline hydrochloride (Dox-T 100 mg) 200 mg for first day followed by 100 mg/day for 4 days and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen), prescribed for 3 days. The patients were recalled after 14 days and sutures removed.
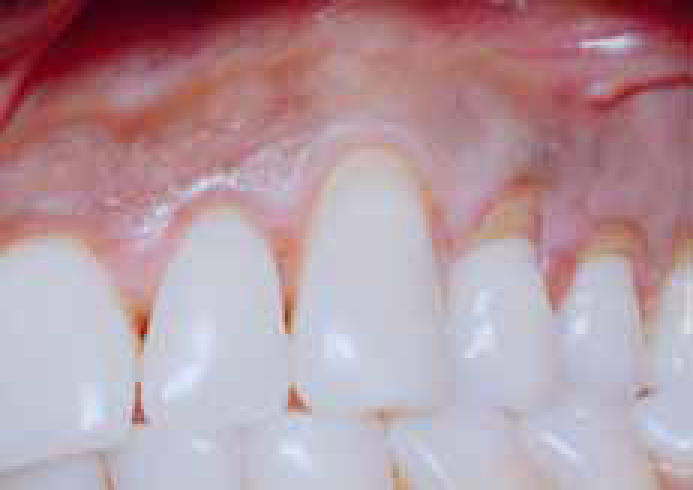
The patients were examined at 4 weeks, 3 months and 6 months post-operatively. The post-operative photographs show complete coverage at 6 months (Figure 4). At the end of 4 years, the treated roots showed complete coverage (Figure 5).
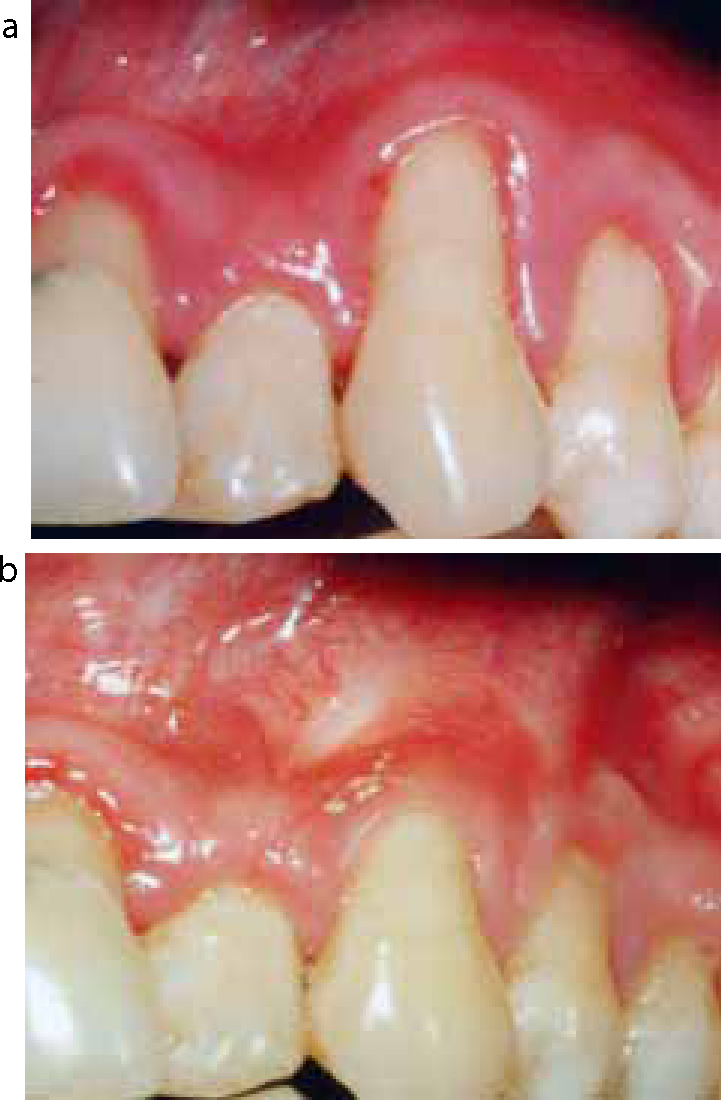

There was a significant reduction in recession and a gain of keratinized gingiva at the end of six months. The gain in clinical attachment level was also significant. No immunologic or antigenic reactions were observed. Long-term, structured, clinical trials are indicated.