Article
Orthodontic retention holds the teeth in the treated position for the period of time necessary to maintain the result and minimise relapse.1 Relapse can be related to physiological recovery, age-related changes and an unstable final occlusion.2 It is acknowledged that spacing is one of the risk factors for post-treatment relapse. This includes pre-restorative orthodontics, whereby space is redistributed for prosthetic tooth replacements.3 Therefore, it is essential for the retention phase of treatment to be planned and discussed with the patient from the outset.
Adhesive bridges are a recognized long-term solution for the fixed replacement of missing teeth after orthodontic treatment. The fabrication and timely placement of a removable retainer after placement of such bridges can be challenging.
The authors' preferred removable retainer is the clear pressure-formed retainer (PFR), which has some evidence suggesting increased patient preference, cost effectiveness and fewer breakages compared with Hawley retainers.4 There is often a delay between the fitting of the bridges and fitting the replacement retainer, ranging from a few days to a few weeks, which can lead to the risk of unwanted tooth movements.
The authors advocate a modified approach to the above that allows placement of the final adhesive bridge and immediate insertion of the clear PFR.
Appointment 1: design (and preparation, if desired) of the adhesive bridge
For impression-making of the arch in which the bridge will be required, the authors recommend the use of a material used for the production of a definitive prosthesis, eg addition silicone, polyether, etc. This impression needs to be fully extended to include all of the teeth in the arch, including the terminal molars. For impression-making of the opposing arch, the authors recommend the use of a standard fast-setting alginate material. Finally, a laboratory prescription for the fabrication of the bridge should be completed.
Appointment 2: trial insertion of the bridge
The bridge should be attached to the abutment tooth to confirm the correct design, marginal adaptation, occlusal prescription and aesthetic outcome. The authors suggest the use of a temporary crown and bridge cementation material to facilitate this. A second laboratory prescription is required for reseating the bridge on the working cast, blocking out the undercuts and fabrication of a clear PFR.
Appointment 3: insertion of the adhesive bridge
The adhesive bridge should be definitively cemented and any excess cement removed.
The clear PFR should then be inserted and checked for adequate retention and patient comfort. The patient's ability to correctly insert and remove the retainer should be confirmed, and dedicated oral hygiene should be provided for the bridge and clear PFR.
Case report
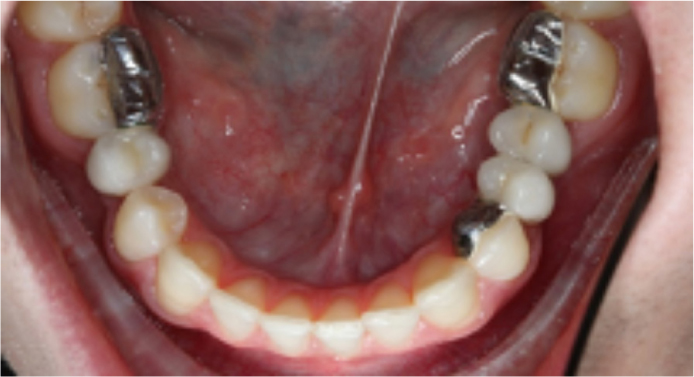
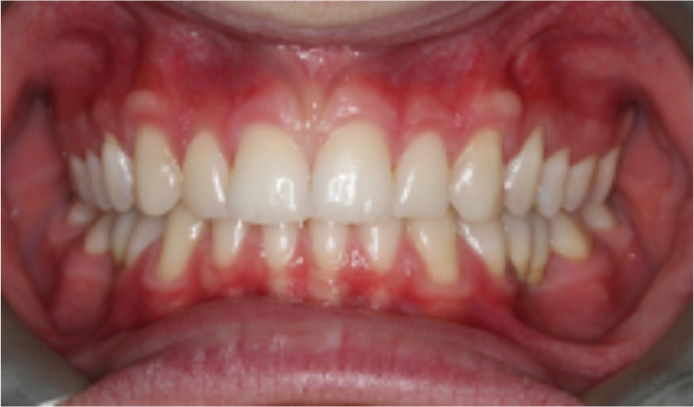
We outline a case that allowed cementation of three cantilevered adhesive bridges and immediate placement of a clear PFR (Figure 1).
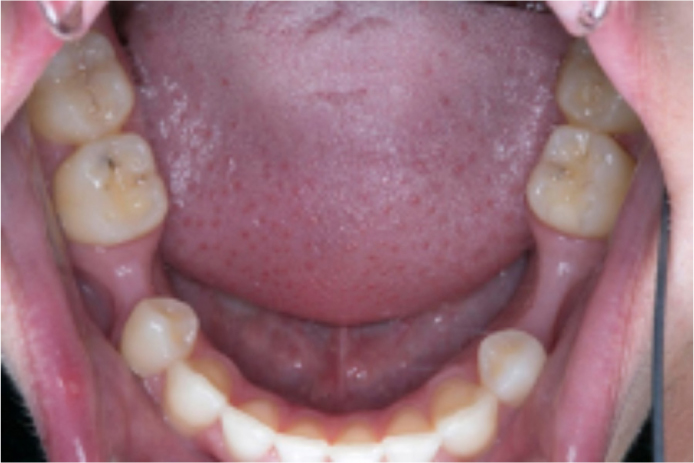
A 14-year-old male patient originally presented to the orthodontic department with a Class II division 1 malocclusion on a skeletal II base with reduced vertical proportions. The malocclusion was complicated by hypodontia of the LR5 and LL5, an increased overjet and overbite. The arches were generally well aligned. His treatment involved growth-modification treatment to address the skeletal discrepancy with a Twin Block functional appliance, followed by upper and lower fixed appliances treatment to redistribute space for the prosthetic replacement of LR5 and LL5. Note that there was more prosthodontic space remaining in the lower left quadrant compared to the lower right quadrant. Impressions of the lower arch were recorded in an additional silicone material and the upper arch was recorded in alginate
The adhesive bridges were replaced accurately on the working cast following trial insertion in the patient's mouth (Figure 2). Note that the cast captures the entirety of the lower arch to allow fabrication of the bridges and the clear PFR.
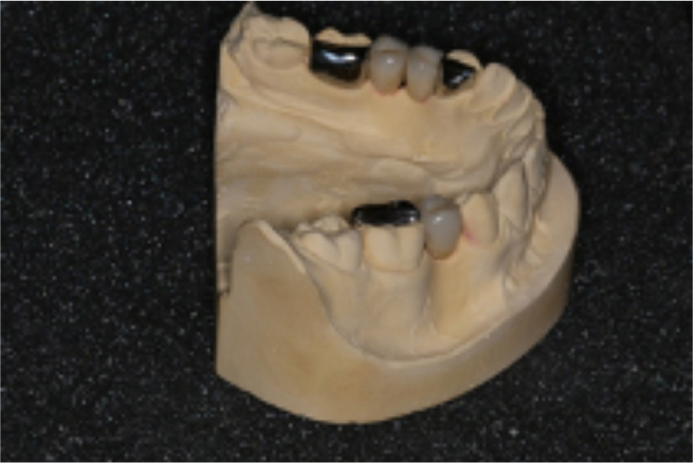
The cast was blocked out with blue light-cured silicone material (Blue-Blokker, Scheu Dental), as with all standard clear PFRs. The pontics had additional, permanently plastic silicone block-out material (Sil-Kitt, Scheu Dental), which blocked out the space under the pontics (Figure 3). The purpose of this was to prevent the thermoplastic material engaging larger undercuts, and thus prevent oral insertion.
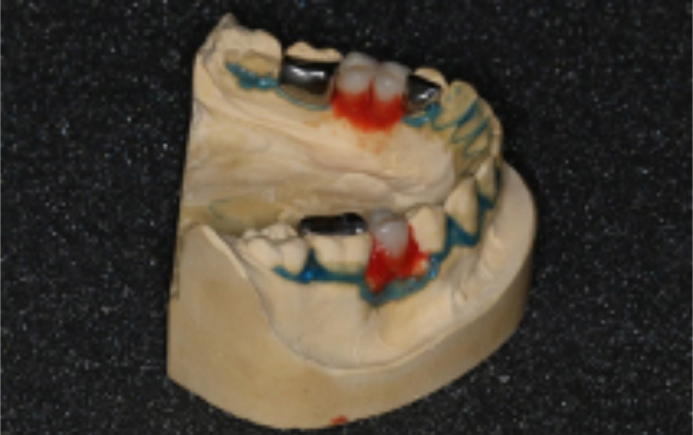
The working cast after fabrication of the clear PFR over the bridges and block out material is shown in Figure 4. The thermoplastic co-polyester was fabricated from a 1-mm thickness blank, and trimmed to 1–2 mm from the gingival margin of the teeth, or base of the ridge in the pontic region.
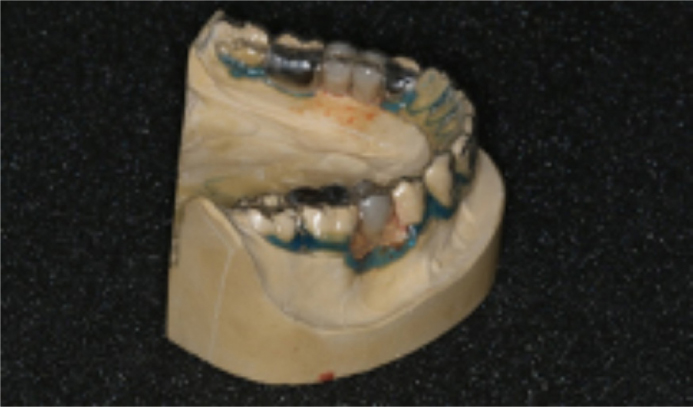
A retracted anterior and occlusal view of the patient after fitting of the three adhesive bridges is shown in Figures 5 and 6. The lower clear PFR was fitted immediately after this and required no modification.